Spaces:
Running
Running
| # Whisper | |
| [[Blog]](https://openai.com/blog/whisper) | |
| [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.04356) | |
| [[Model card]](https://github.com/openai/whisper/blob/main/model-card.md) | |
| [[Colab example]](https://colab.research.google.com/github/openai/whisper/blob/master/notebooks/LibriSpeech.ipynb) | |
| Whisper is a general-purpose speech recognition model. It is trained on a large dataset of diverse audio and is also a multitasking model that can perform multilingual speech recognition, speech translation, and language identification. | |
| ## Approach | |
| 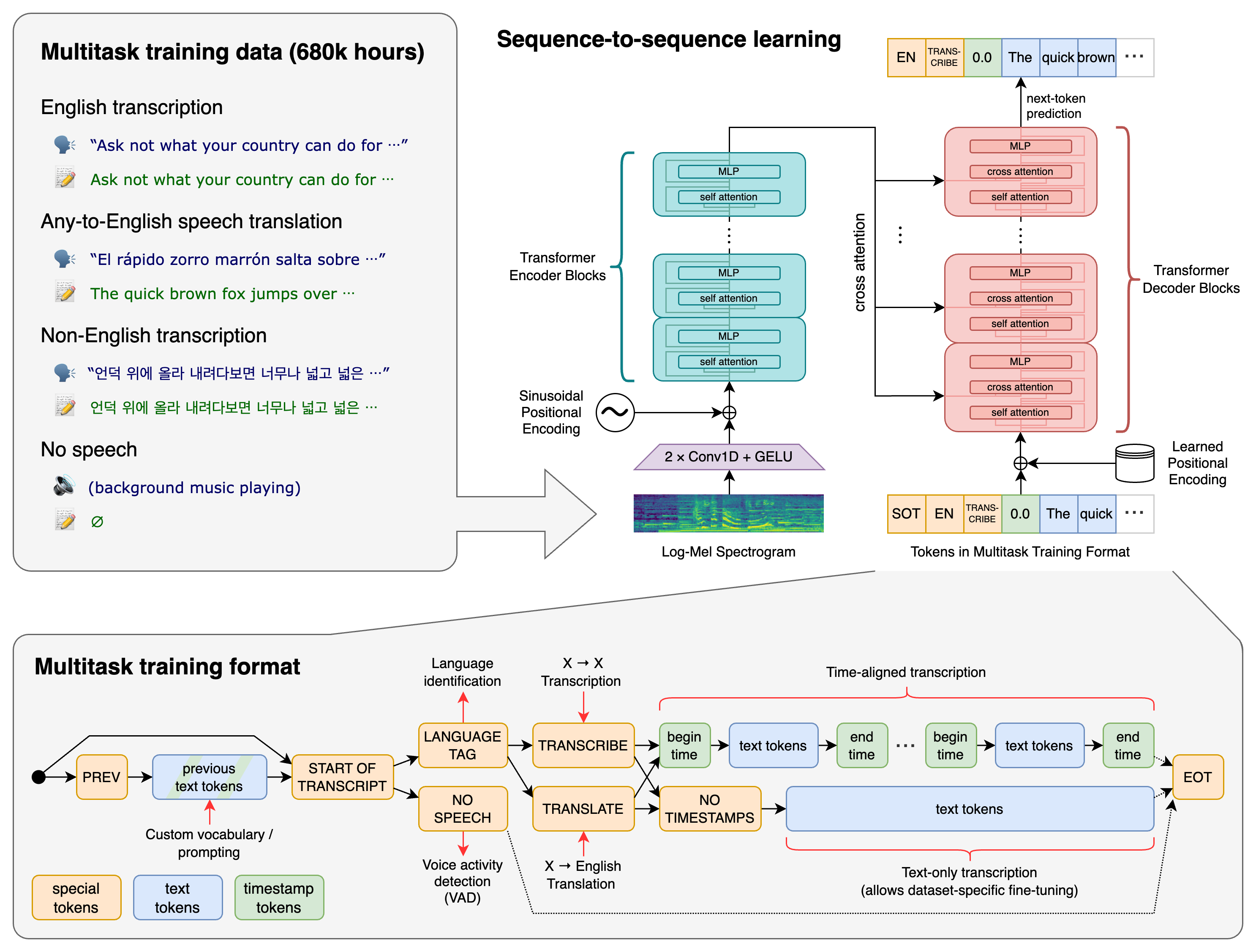 | |
| A Transformer sequence-to-sequence model is trained on various speech processing tasks, including multilingual speech recognition, speech translation, spoken language identification, and voice activity detection. These tasks are jointly represented as a sequence of tokens to be predicted by the decoder, allowing a single model to replace many stages of a traditional speech-processing pipeline. The multitask training format uses a set of special tokens that serve as task specifiers or classification targets. | |
| ## Setup | |
| We used Python 3.9.9 and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) 1.10.1 to train and test our models, but the codebase is expected to be compatible with Python 3.8-3.10 and recent PyTorch versions. The codebase also depends on a few Python packages, most notably [HuggingFace Transformers](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index) for their fast tokenizer implementation and [ffmpeg-python](https://github.com/kkroening/ffmpeg-python) for reading audio files. You can download and install (or update to) the latest release of Whisper with the following command: | |
| pip install -U openai-whisper | |
| Alternatively, the following command will pull and install the latest commit from this repository, along with its Python dependencies: | |
| pip install git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.git | |
| To update the package to the latest version of this repository, please run: | |
| pip install --upgrade --no-deps --force-reinstall git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.git | |
| It also requires the command-line tool [`ffmpeg`](https://ffmpeg.org/) to be installed on your system, which is available from most package managers: | |
| ```bash | |
| # on Ubuntu or Debian | |
| sudo apt update && sudo apt install ffmpeg | |
| # on Arch Linux | |
| sudo pacman -S ffmpeg | |
| # on MacOS using Homebrew (https://brew.sh/) | |
| brew install ffmpeg | |
| # on Windows using Chocolatey (https://chocolatey.org/) | |
| choco install ffmpeg | |
| # on Windows using Scoop (https://scoop.sh/) | |
| scoop install ffmpeg | |
| ``` | |
| You may need [`rust`](http://rust-lang.org) installed as well, in case [tokenizers](https://pypi.org/project/tokenizers/) does not provide a pre-built wheel for your platform. If you see installation errors during the `pip install` command above, please follow the [Getting started page](https://www.rust-lang.org/learn/get-started) to install Rust development environment. Additionally, you may need to configure the `PATH` environment variable, e.g. `export PATH="$HOME/.cargo/bin:$PATH"`. If the installation fails with `No module named 'setuptools_rust'`, you need to install `setuptools_rust`, e.g. by running: | |
| ```bash | |
| pip install setuptools-rust | |
| ``` | |
| ## Available models and languages | |
| There are five model sizes, four with English-only versions, offering speed and accuracy tradeoffs. Below are the names of the available models and their approximate memory requirements and relative speed. | |
| | Size | Parameters | English-only model | Multilingual model | Required VRAM | Relative speed | | |
| |:------:|:----------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:-------------:|:--------------:| | |
| | tiny | 39 M | `tiny.en` | `tiny` | ~1 GB | ~32x | | |
| | base | 74 M | `base.en` | `base` | ~1 GB | ~16x | | |
| | small | 244 M | `small.en` | `small` | ~2 GB | ~6x | | |
| | medium | 769 M | `medium.en` | `medium` | ~5 GB | ~2x | | |
| | large | 1550 M | N/A | `large` | ~10 GB | 1x | | |
| The `.en` models for English-only applications tend to perform better, especially for the `tiny.en` and `base.en` models. We observed that the difference becomes less significant for the `small.en` and `medium.en` models. | |
| Whisper's performance varies widely depending on the language. The figure below shows a WER (Word Error Rate) breakdown by languages of the Fleurs dataset using the `large-v2` model. More WER and BLEU scores corresponding to the other models and datasets can be found in Appendix D in [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.04356). The smaller, the better. | |
|  | |
| ## Command-line usage | |
| The following command will transcribe speech in audio files, using the `medium` model: | |
| whisper audio.flac audio.mp3 audio.wav --model medium | |
| The default setting (which selects the `small` model) works well for transcribing English. To transcribe an audio file containing non-English speech, you can specify the language using the `--language` option: | |
| whisper japanese.wav --language Japanese | |
| Adding `--task translate` will translate the speech into English: | |
| whisper japanese.wav --language Japanese --task translate | |
| Run the following to view all available options: | |
| whisper --help | |
| See [tokenizer.py](https://github.com/openai/whisper/blob/main/whisper/tokenizer.py) for the list of all available languages. | |
| ## Python usage | |
| Transcription can also be performed within Python: | |
| ```python | |
| import whisper | |
| model = whisper.load_model("base") | |
| result = model.transcribe("audio.mp3") | |
| print(result["text"]) | |
| ``` | |
| Internally, the `transcribe()` method reads the entire file and processes the audio with a sliding 30-second window, performing autoregressive sequence-to-sequence predictions on each window. | |
| Below is an example usage of `whisper.detect_language()` and `whisper.decode()` which provide lower-level access to the model. | |
| ```python | |
| import whisper | |
| model = whisper.load_model("base") | |
| # load audio and pad/trim it to fit 30 seconds | |
| audio = whisper.load_audio("audio.mp3") | |
| audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio) | |
| # make log-Mel spectrogram and move to the same device as the model | |
| mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio).to(model.device) | |
| # detect the spoken language | |
| _, probs = model.detect_language(mel) | |
| print(f"Detected language: {max(probs, key=probs.get)}") | |
| # decode the audio | |
| options = whisper.DecodingOptions() | |
| result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options) | |
| # print the recognized text | |
| print(result.text) | |
| ``` | |
| ## More examples | |
| Please use the [🙌 Show and tell](https://github.com/openai/whisper/discussions/categories/show-and-tell) category in Discussions for sharing more example usages of Whisper and third-party extensions such as web demos, integrations with other tools, ports for different platforms, etc. | |
| ## License | |
| Whisper's code and model weights are released under the MIT License. See [LICENSE](https://github.com/openai/whisper/blob/main/LICENSE) for further details. |